Blockchain & Open Finance: An Overview
Processing financial transactions without intermediaries using decentralized systems that are secure, transparent, tamper-proof, and open-source.
Executive Summary
This article introduces blockchain technology as an innovative concept that provides a secure and tamper-proof way to create decentralized systems that eliminate the need for intermediaries. Since the first real-world implementation of the concept in 2009, blockchains have now been widely adopted in the financial services industry. Through a series of question-and-answer discussions, this article looks at how a blockchain works and where it can best be used. Finally, we highlight the strong connections between blockchain and open-source and open standards in finance.
Introduction
Blockchain is a powerful technology that improves security, transparency, and trust across various industries. It enables decentralized systems, prevents data tampering, and eliminates the need for intermediaries. From cryptocurrencies and smart contracts to supply chain and healthcare, blockchain offers innovative solutions to modern challenges. In this article we introduce blockchain technology by answering the following questions: What is a blockchain? How does the blockchain work? Why use a blockchain? How do I decide when to use a blockchain? Next, we examine leading open-source blockchain platforms. Finally, we look at a few blockchain platforms designed specifically for the financial services industry.
What Is A Blockchain?
A blockchain is a digital system for recording and storing information in a way that is secure, transparent, and cannot be modified. Imagine a chain of blocks, where each block contains a group of records or transactions, and every block is linked to the one before it using complex mathematical techniques called cryptography. Unlike traditional systems where one central authority (like a bank) controls the data, blockchain operates on a decentralized network of computers. The Keywords section at the end of this article provides definitions of the italicized terms used in this article. This means everyone on the network has a copy of the entire record, and they work together to verify and agree on new entries through a process called consensus. Once information is added to a block and linked to the chain, it cannot be changed or deleted, that is the information is immutable; this making blockchain highly secure and trustworthy. It is widely used in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, but its applications extend to many areas, such as managing digital identities, tracking supply chains, securing medical records, and even creating automated (smart) contracts. By eliminating the need for intermediaries, blockchain ensures transparency, enhances trust, and reduces the risk of fraud or manipulation.
How Does The Blockchain Work?
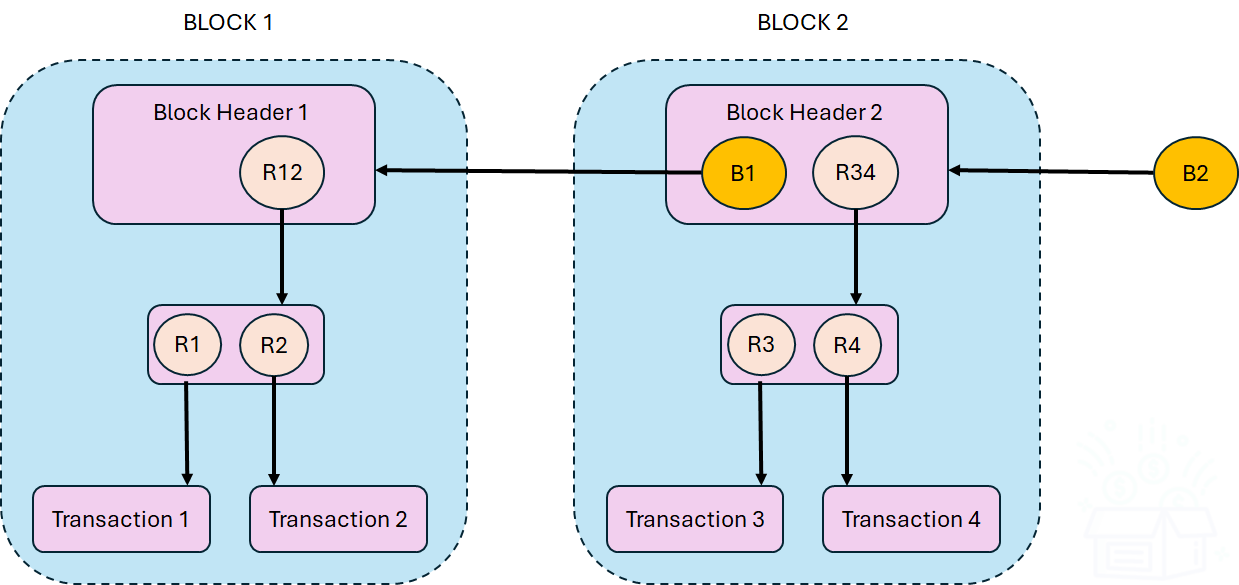
In this section we present a simplified description of how a blockchain works from a data storage perspective. Figure 1 shows a simplified blockchain data structure that has been adapted from Drescher1. The simplified blockchain-data-structure consists of two blocks labeled BLOCK 1 and BLOCK 2. Both blocks contain block headers labeled Block Header 1 and Block Header 2, respectively. BLOCK 1 is the very first block in this data structure (i.e. blockchain), hence, it does not have a preceding block, and, consequently, Block Header 1 does not contain any reference to a preceding block header. That is BLOCK 1 does now have an orange circle with a secure address or reference of the previous block. When talking to technical folks each of these secure addresses will be referred to as a hash or digest. Since BLOCK 2 has a predecessor, Block Header 2 maintains a hash to its preceding block header labeled as B1. R1 and R2 are hashes of the data for Transaction 1 and Transaction 2, respectively. R1 and R2 are hashed to create R12 the hash of all the transaction in the block.
Two important things to note here, firstly, the process that takes data and generates a secure address or hash of that data operates in one direction only, as shown in Figure 22. What this means is that, if I have the data I can use the SHA-1 hash function to recreate the hash, but if I have the hash, I cannot recreate the data.
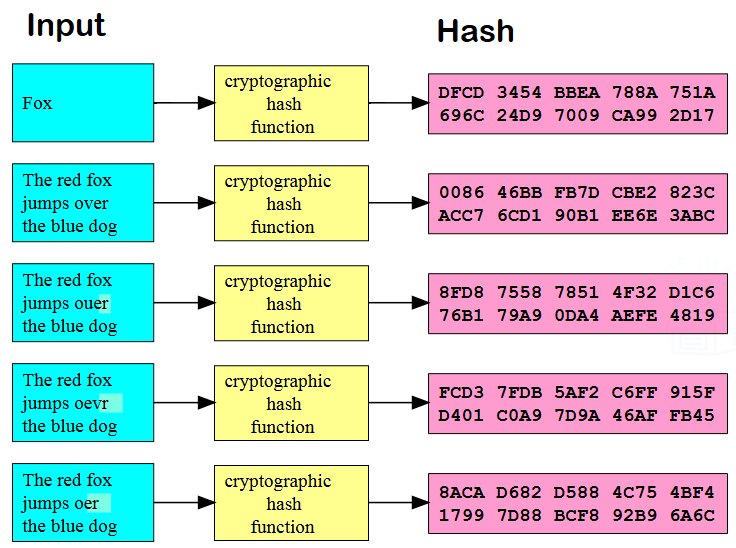
Secondly, should the data in Transaction 1 or Transaction 2 be modified in any way then R1 or R2 will change and as a result the hash of Block Header 1 will no longer be B1, so BLOCK 2 will no longer be chained to BLOCK 1.
Why Use A Blockchain?
Blockchain is highlighted as a transformative technology due to its ability to address critical challenges related to security, transparency, and efficiency. Blockchain provides a decentralized system where data is stored securely and cannot be altered, eliminating the need for intermediaries and ensuring trust among participants. In the metaverse, blockchain ensures data privacy, asset management, and platform interoperability, fostering seamless digital ecosystems. For financial systems, it offers secure and transparent solutions for cross-border payments, cryptocurrencies, and smart contracts, reducing reliance on centralized authorities and enhancing efficiency. Blockchain is also leveraged in healthcare and supply chain management industries to ensure tamper-proof records, improve transparency, and streamline processes. Additionally, its flexibility in permissioned and permissionless models allows tailored applications for regulated industries like finance and healthcare. Across all use cases, blockchain's core features—decentralization, immutability, and transparency—make it a powerful tool for fostering trust, innovation, and collaboration in multi-stakeholder environments.
Where To Use A Blockchain?
Blockchain can be used in various ways depending on the industry and application. Here's how it is typically utilized:
Cryptocurrencies: Blockchain powers digital currencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Users can securely send, receive, and store digital money without relying on banks or intermediaries. It also ensures transparency and prevents fraud, such as attempts to double-spend when using a digital currency.
Smart Contracts: Blockchain allows for self-executing contracts where terms are written into code. These smart contracts automatically execute when predefined conditions are met, reducing the need for middlemen in agreements like loans, insurance claims, or real estate transactions.
Supply Chain Management: Companies use blockchain to track goods throughout their supply chain. It ensures transparency, authenticity, and traceability, helping reduce fraud and improve efficiency in industries like retail, agriculture, and manufacturing.
Healthcare: Blockchain secures patient records, allowing only authorized parties to access and share data. It improves privacy, reduces errors, and ensures data integrity for medical histories, prescriptions, and diagnostic information.
Identity Management: Blockchain helps individuals control their digital identities securely. It prevents identity theft and simplifies verification processes for accessing services like banking, education, or government programs.
Voting Systems: Blockchain can create secure, transparent, and tamper-proof voting systems. Each vote is recorded on the blockchain, ensuring accuracy and eliminating fraud.
Asset Ownership: Blockchain records ownership of digital and physical assets, such as real estate, intellectual property, or art. It creates a transparent and unalterable history of ownership and transfers.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Blockchain enables financial services like lending, borrowing, and investing without traditional intermediaries, providing faster, more accessible, and transparent financial solutions.
Energy Management: Blockchain facilitates peer-to-peer energy trading, where individuals can sell excess energy from renewable sources like solar panels to others in their community.
Gaming and NFTs: Blockchain is used in gaming for virtual goods ownership and non-fungible tokens (NFTs), which represent unique digital assets like art, collectibles, or in-game items.
How Do I Decide When To Use A Blockchain?
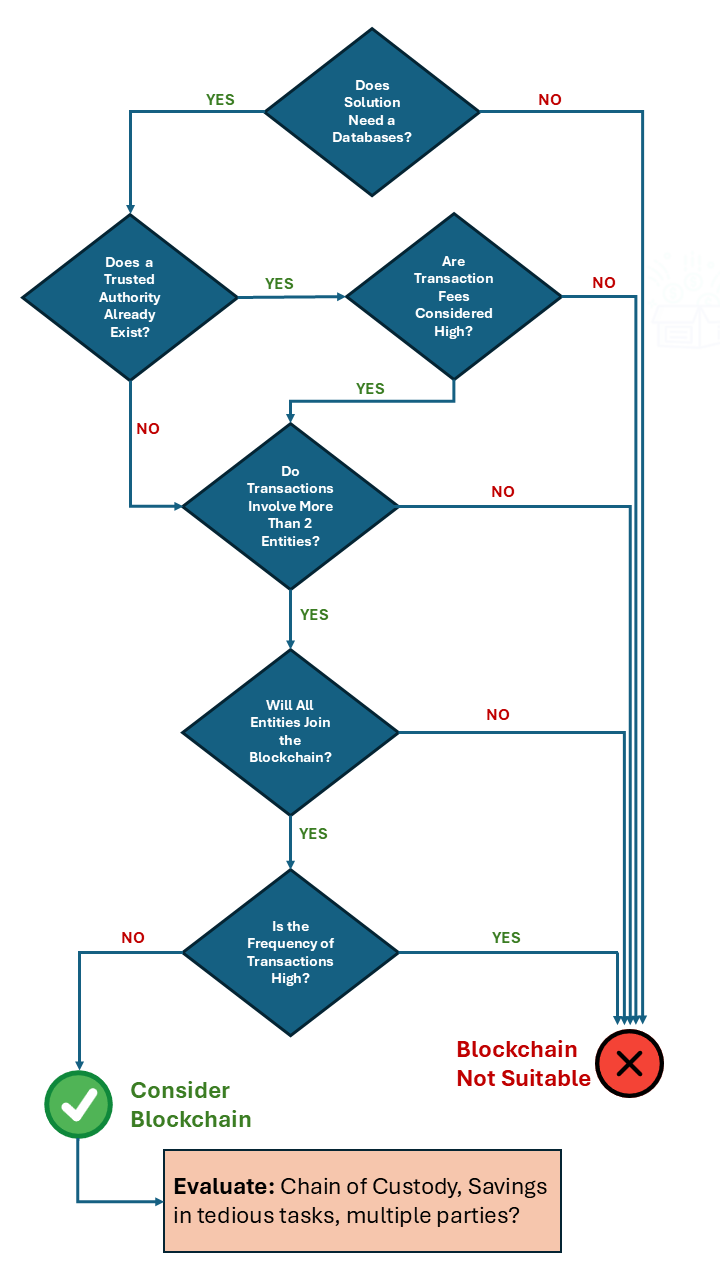
The blockchain is not the ideal solution to every problem in finance. Below we present a decision model adapted from Yiu3 that may be used to decide if it is appropriate for you to use the blockchain in your solution.
Leading Open Source Blockchain Platforms
Many well-known blockchain platforms are supported by an open-source community. Below is a list and descriptions of six leading open source blockchain platforms from Ashutosh Dubey4.
Ethereum: Ethereum is a decentralized, open-source blockchain platform that supports smart contracts and the development of decentralized applications (dApps). It uses its native cryptocurrency called Ether (ETH) and is known for its programmable functionality, which allows developers to build complex applications on top of the blockchain.
Hyperledger Fabric: Hyperledger Fabric is an open-source permissioned blockchain platform developed by the Linux Foundation. It provides a modular architecture that enables enterprises to build private, scalable, and secure blockchain networks. Fabric supports smart contracts written in various programming languages and offers features like channel-based privacy, flexible consensus mechanisms, and membership services.
Corda: Corda is an open-source blockchain platform designed for enterprise use cases. It focuses on privacy and security by using a permissioned network architecture. Corda enables businesses to transact directly, securely, and privately using smart contracts. It also provides a unique “notary” service for validating transactions without exposing sensitive data.
Stellar: Stellar is an open-source blockchain platform designed for cross-border transactions and digital asset issuance. It offers fast, low-cost transactions and supports the creation of tokens and assets on the network. Stellar uses a consensus protocol called the Stellar Consensus Protocol (SCP) and has a built-in decentralized exchange for asset trading.
IOTA: IOTA is an open-source blockchain platform specifically designed for the Internet of Things (IoT). It utilizes a directed acyclic graph (DAG) called the Tangle instead of a traditional blockchain. IOTA aims to provide a scalable, fee-less, and secure infrastructure for machine-to-machine transactions and data transfer in IoT ecosystems.
Tezos: Tezos is an open-source blockchain platform that features a self-amending governance mechanism. It allows stakeholders to vote on proposed protocol upgrades without the need for hard forks. Tezos supports smart contracts and offers formal verification, a technique for mathematically proving the correctness of the code.
Some Applications Of Blockchains In Finance
In this section we present a few blockchain platforms designed specifically for the financial services industry.
Consensys Quorum: Quorum is an enterprise-variant of the Ethereum blockchain that was developed by JP Morgan Chase. It was acquired by Consensys in August 2020. Quorum is an open-source project that incorporates features like private transactions, network permissions, and enhanced data privacy. This platform is widely used in industries such as finance and supply chain management, where privacy and confidentiality are critical.
R3 Corda: The R3 Corda blockchain platform was designed for the financial services industry, particularly around trade finance. With R3 Corda parties can securely share trade documents like letters of credit and invoices.
Ripple: Ripple is a blockchain-based digital payment network and protocol that uses the XRP Ledger (XRPL), an open-source, permissionless and decentralized blockchain technology and XRP, XRP is a digital asset that’s native to the XRPL. Ripple generates revenue by providing cross-border payment and crypto liquidity services to businesses.
Conclusion
Blockchain is a powerful technology that improves security, transparency, and trust across various industries. It enables decentralized systems, prevents data tampering, and eliminates the need for intermediaries. From cryptocurrencies and smart contracts to supply chain and healthcare, blockchain offers innovative solutions to modern challenges. We looked at how a blockchain works and where it can best be used. Finally, we highlighted the strong connections between blockchain and open-source and open standards in finance.
Keywords
Here is list of describing nine keywords used in this article.
Cryptography: Using advanced math to protect information, ensuring only authorized people can access it.
Decentralized Network: A system where no single person or organization controls the data; instead, all users work together to maintain it.
Consensus: An agreement among all participants in the network to verify and validate data before adding it to the blockchain.
Immutable: Once data is added to the blockchain, it cannot be changed or deleted, ensuring trust and security.
Transactions: The actions or exchanges recorded in the blockchain, such as payments, contracts, or data transfers.
Transparency: Everyone in the network can see and verify the stored information, making it trustworthy.
Cryptocurrencies: Digital money, like Bitcoin, that uses blockchain to operate securely without a bank or intermediary.
Permissionless Blockchain: Is a public blockchain platform that is fully decentralized and open to all. Anyone can validate data and participate in consensus on the platform.
Permissioned Blockchain: Is a blockchain platform where every user must have a verified identity, that is it is not a public platform.
D. Drescher (2017). Storing Transaction Data. In: Blockchain Basics. Apress, Berkeley, CA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4842-2604-9_14
Wikipedia contributors. (2025, January 14). Cryptographic hash function. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved February 1, 2025, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Cryptographic_hash_function&oldid=1269396313
S.M. Yiu, "Selection Criteria for Blockchain Applications" in HKUx: Blockchain and FinTech: Basics, Applications, and Limitations. Online [Available] https://www.edx.org/learn/blockchain/university-of-hong-kong-blockchain-and-fintech-basics-applications-and-limitations
A. Dubey (2023, June 6). Open source blockchain platforms. Medium. https://medium.com/@wonderful_lilac_beetle_302/open-source-blockchain-platforms-6c00bb38858f