Introducing Sossy - A Secure Open-Source Software Supply Chain Project
The sossy-crawler generates a complete dependency graph for Linux executables and shared libraries.
Introduction
In this article we introduce Sossy, a secure open-source software supply chain project. We describe the first component of this project, the Sossy-crawler, a dependency graph generator for Linux executable (ELF) files and shared library object (.so) files. This is an extension of an earlier article titled “A Framework for a Secure Open-Source Software Supply Chain”. We plan to release Sossy as an open-source project on GitHub.
The Sossy-crawler
Sossy-crawler was written using the bash scripting language and it depends on five other open-source utilities and applications – Objdump, sed, lddtree, Graphviz, and PostgreSQL. The Sossy-crawler takes an input a list of files to be analyzed or a directory such as /usr/bin or /usr/sbin. It then builds a complete dependency graph for each application, as well as a graph of all the applications. The dependency graphs are directed graphs (digraph) and may be output as simple digraphs or weighted digraphs where the edges are labeled with frequency of source to sink calls.
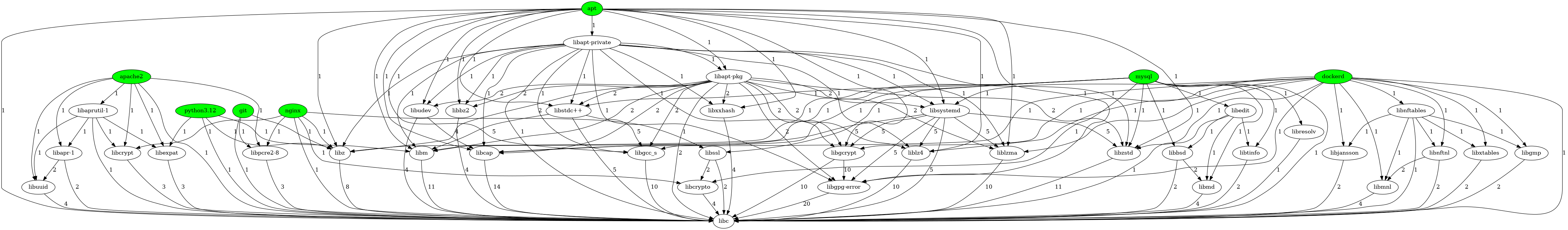
Next, we present some outputs as simple and labeled graphs of the Sossy-crawler for the following applications: mysql, dockerd, apt, apache2, nginx, python3.12, and git running on Ubuntu 24.04. The parent application nodes have a green fill.
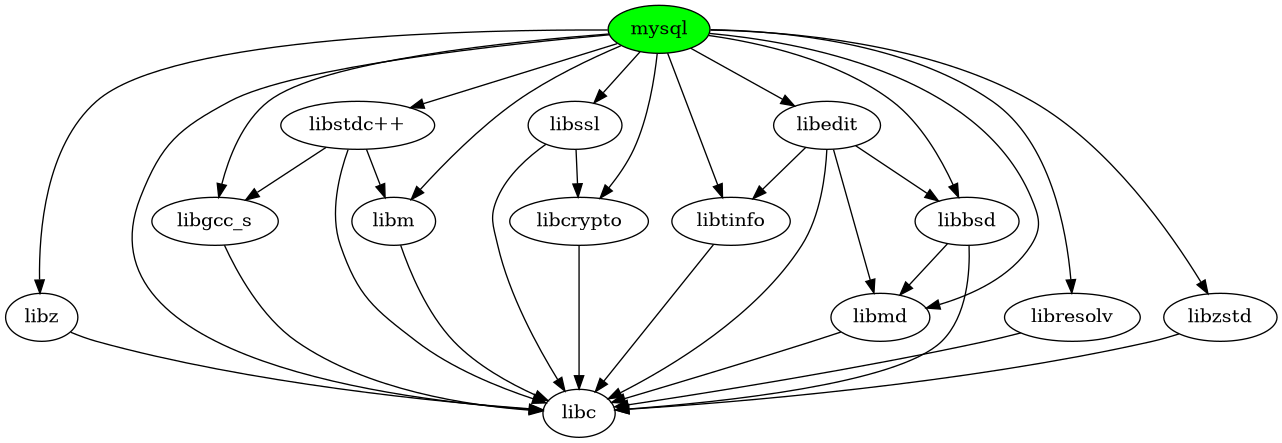
The simple and weighted graphs for mysql.
Figure 1 and Figure 2 show that mysql has 13 direct dependencies and 11 transitive dependencies that finally depend on libc.
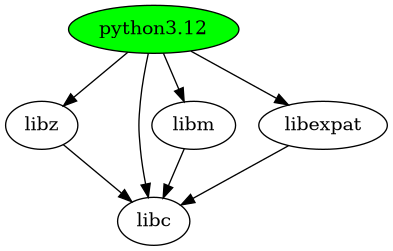
Figure 3 shows that python 3.12 has 4 direct dependencies: libc, libz, libm and libexpat; and the last three depend on libc.
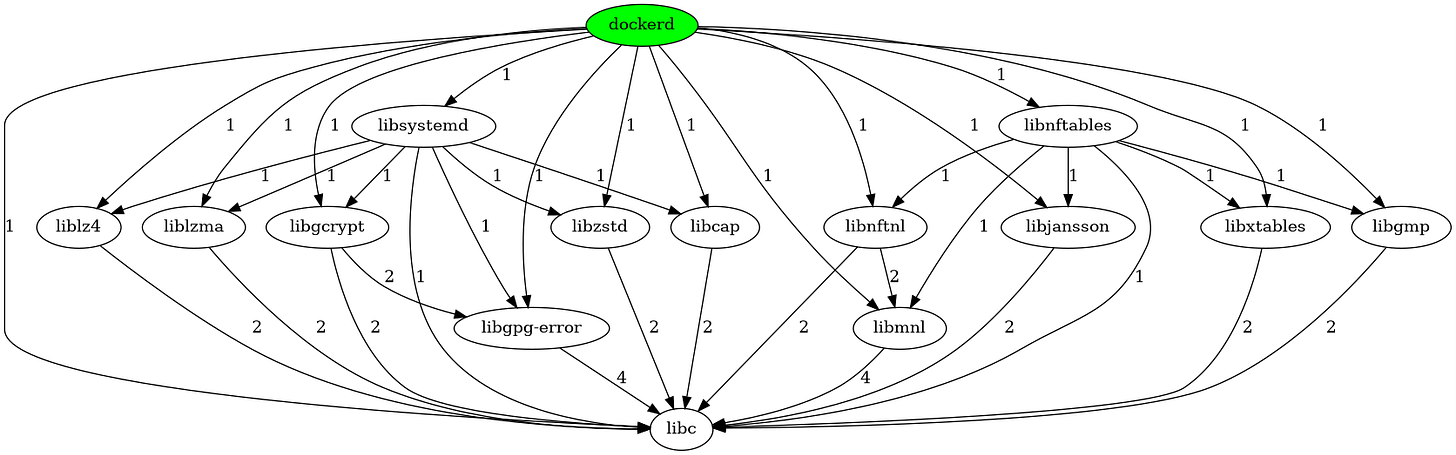
Figure 4 shows that dockerd has 13 direct dependencies and 15 transitive dependencies, and all components in this dependency relationship depend on libc.
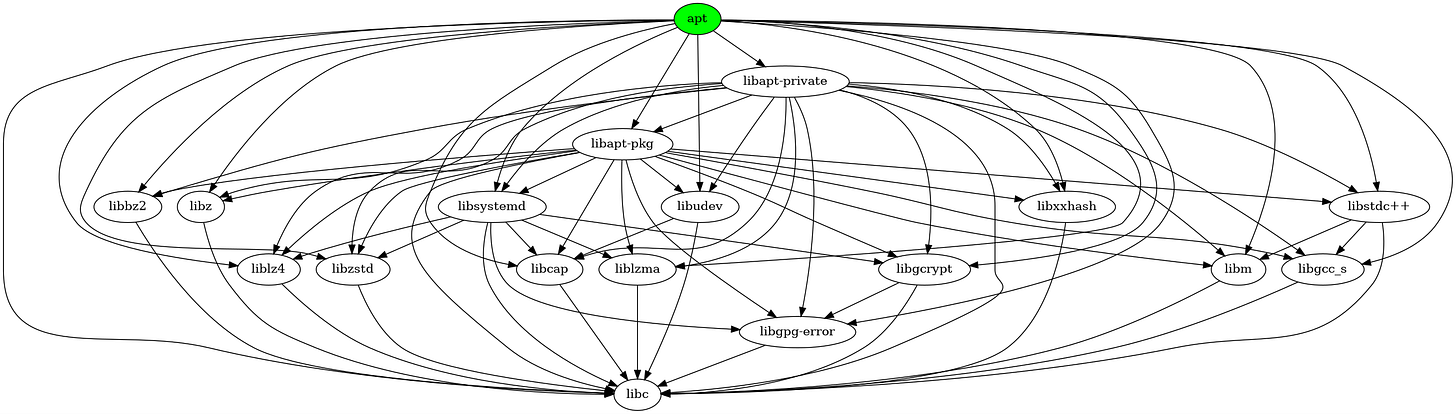
Figure 5 shows that apt has 10 direct dependencies and 17 transitive dependencies, and all components in this dependency relationship depend on libc.
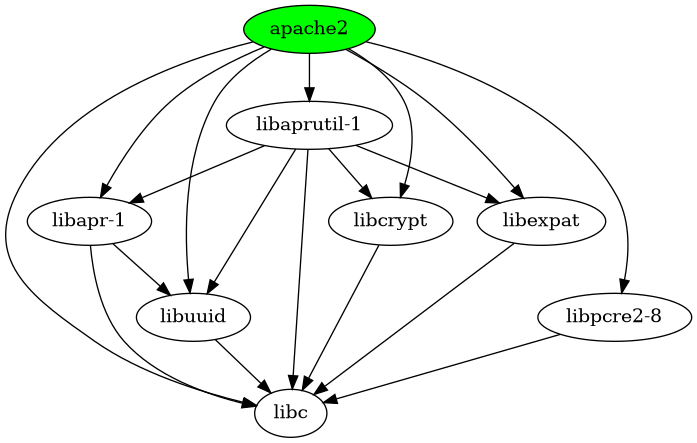
Apache 2 is a widely used, open-source web server software. It was developed by the Apache Software Foundation and is designed to run on a variety of operating systems such as Windows, Linux, and macOS1. Figure 6 shows that apache2 has 7 direct dependencies and 7 transitive dependencies, and all components in this dependency relationship depend on libc.
nginx ("engine x") is an HTTP web server, reverse proxy, content cache, load balancer, TCP/UDP proxy server, and mail proxy server2. Figure 7 shows that nginx has 6 direct dependencies and 5 transitive dependencies, and all components in this dependency relationship depend on libc.
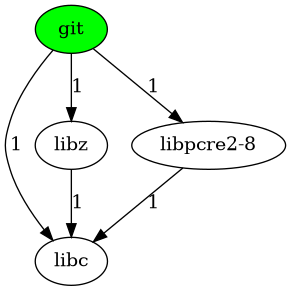
Figure 8 shows that git has 3 direct dependencies and 2 transitive dependencies, and all components in this dependency relationship depend on libc.
Discussion
From the graphs above the criticality of the GNU C library (libc) becomes obvious as all other nodes have a dependency on this node. If this node is compromised, it can have an impact on all other applications and shared libraries. According to the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE™) Program, here are some recent vulnerabilities to this library.
CVE-2025-15281 (2026): A DoS vulnerability in
wordexpaffecting versions 2.0 to 2.42, causing process abortion due to improper flag handling.CVE-2025-4802 (2025): A local privilege escalation flaw in versions 2.27 to 2.38 allowed attackers to load malicious libraries via
LD_LIBRARY_PATHin setuid binaries.CVE-2024-2961 (2024): A buffer overflow in the
iconv()function, affecting versions 2.39 and older, allowing potential remote code execution (RCE).CVE-2023-6246 (2024): A heap-based buffer overflow in the
__vsyslog_chkfunction, leading to local root privilege escalation. This issue affects glibc 2.36 and newer.
It is obvious that we have quite a number of important applications such as the ones analyzed using Sossy-crawler that are heavily reliant on libc despite the fact that libc has well-known and published vulnerabilities. There are even older vulnerabilities such CVE-2017-6509 (Heap Overflow in glibc), and CVE-2019-19126 (Potential for Buffer Overflow) that may be present if using unpatched versions of libc. An important improvement to Sossy-crawler is to report more information to include, supplier name, component name, the component version, dependency relationship, author, etc. One recommendation would be to follow the NTIA minimum requirements (Halbritter and Merli, 2024) for SBOM tool output3.
Conclusion
In this article we introduced the Sossy, a secure open-source software supply chain project. We discussed the Sossy-crawler, which is the first component of this project.
The Sossy-crawler allows us to create complete dependency graphs for ELF-based applications and shared objects. This can be used to study the impact of one node across different applications and shared libraries. The weighted versions of the dependency graphs allow us to evaluate the criticality of certain paths and nodes.
Next, we proceed to do more detailed network analysis using these digraphs for upcoming research articles based on this work.
What is Apache 2? https://www.hostwinds.com/tutorials/apache-2-web-server
nginx. https://nginx.org/en/
Andreas Halbritter and Dominik Merli. 2024. Accuracy Evaluation of SBOM Tools for Web Applications and System-Level Software. In The 19th International Conference on Availability, Reliability and Security (ARES 2024), July 30--August 02, 2024, Vienna, Austria. ACM, New York, NY, USA 9 Pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3664476.3670926






Great visualization of the libc singleppoint of failure problem. The weighted graphs showing call frequency are particularly useful for risk assessment since not all dependencies carry equal criticality in practce. Would love to see how Sossy handles circular dependencies if they show up in more complex application ecosystems.